Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
High Voltage Generator System#
This example demonstrates the HighVoltageGeneratorSystem which calculates operating window constraints for the pulse power generator.
==================================================
High Voltage Generator System
==================================================
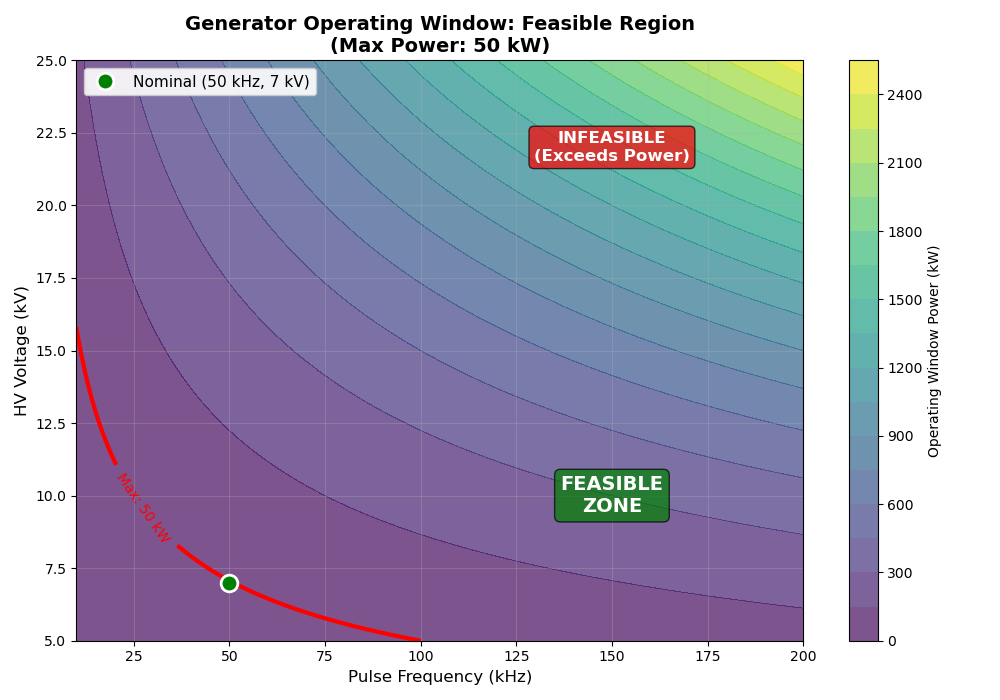
Operating Window Power: 49000.0 W
Operating Window Satisfied: Yes
==================================================
[OK] Operating point is within generator capability
Generating plot: Operating Zone (Voltage vs Frequency)...
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import openmdao.api as om
from paroto.systems.generator import HighVoltageGeneratorSystem
# Create OpenMDAO problem
prob = om.Problem()
prob.model.add_subsystem(
"generator",
HighVoltageGeneratorSystem(
design_impedance=50.0, # 50 Ohm
pulse_duration=1e-6, # 1 μs
max_power=50000.0, # 50 kW limit
),
promotes=["*"],
)
prob.setup()
# Set operating parameters
prob.set_val("pulse_frequency", 50000.0) # 50 kHz
prob.set_val("hv_voltage", 7000.0) # 7 kV (within feasible zone)
# Run model
prob.run_model()
# Extract results
power = prob.get_val("operating_window_power")[0]
satisfied = prob.get_val("hv_operating_window_satisfied")[0]
print("=" * 50)
print("High Voltage Generator System")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"Operating Window Power: {power:.1f} W")
print(f"Operating Window Satisfied: {'Yes' if satisfied > 0.5 else 'No'}")
print("=" * 50)
if satisfied > 0.5:
print("[OK] Operating point is within generator capability")
else:
print("[FAIL] Operating point exceeds generator limits")
print(" Reduce frequency or voltage to stay within operating window")
# Plot operating zone: Voltage vs Frequency
print("\nGenerating plot: Operating Zone (Voltage vs Frequency)...")
freq_range = np.linspace(10e3, 200e3, 100) # 10 kHz to 200 kHz
voltage_range = np.linspace(5e3, 25e3, 100) # 5 kV to 25 kV
max_power = 50000.0 # W
# Create meshgrid
F, V = np.meshgrid(freq_range, voltage_range)
# Calculate operating window power for each (f, V) combination
# P_window = f * V^2 * t_pulse / Z
Z = 50.0 # Ohm
t_pulse = 1e-6 # s
P_window = F * V**2 * t_pulse / Z
# Create constraint satisfaction map (1 if feasible, 0 if not)
constraint_satisfied = (P_window <= max_power).astype(float)
# Create the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 7))
# Contour plot showing operating window power levels
contour = ax.contourf(F / 1e3, V / 1e3, P_window / 1e3, levels=20, cmap="viridis", alpha=0.7)
cbar = plt.colorbar(contour, ax=ax, label="Operating Window Power (kW)")
# Add boundary line at max power
boundary_contour = ax.contour(
F / 1e3, V / 1e3, P_window / 1e3, levels=[max_power / 1e3], colors="red", linewidths=3
)
ax.clabel(boundary_contour, inline=True, fontsize=10, fmt="Max: %.0f kW")
# Shade the feasible region
feasible_mask = P_window <= max_power
ax.contourf(
F / 1e3,
V / 1e3,
feasible_mask.astype(float),
levels=[0.5, 1.5],
colors=["none"],
hatches=[""],
alpha=0,
)
# Mark the nominal operating point
ax.plot(
50,
7,
"go",
markersize=12,
markeredgewidth=2,
markeredgecolor="white",
label="Nominal (50 kHz, 7 kV)",
zorder=10,
)
# Add labels for feasible/infeasible regions
ax.text(
150,
10,
"FEASIBLE\nZONE",
fontsize=14,
fontweight="bold",
color="white",
ha="center",
va="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", facecolor="green", alpha=0.7),
)
ax.text(
150,
22,
"INFEASIBLE\n(Exceeds Power)",
fontsize=12,
fontweight="bold",
color="white",
ha="center",
va="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", facecolor="red", alpha=0.7),
)
ax.set_xlabel("Pulse Frequency (kHz)", fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel("HV Voltage (kV)", fontsize=12)
ax.set_title(
"Generator Operating Window: Feasible Region\n(Max Power: 50 kW)",
fontsize=14,
fontweight="bold",
)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.legend(loc="upper left", fontsize=11, framealpha=0.9)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.224 seconds)